前言
题单LeetCode 热题 100的栈部分,给出解析。
20. Valid Parentheses
题目描述
Given a string s containing just the characters '(', ')', '{', '}', '[' and ']', determine if the input string is valid.
An input string is valid if:
- Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
- Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
- Every close bracket has a corresponding open bracket of the same type.
Example 1:
1 | Input: s = "()" |
Example 2:
1 | Input: s = "()[]{}" |
Example 3:
1 | Input: s = "(]" |
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 10^4sconsists of parentheses only'()[]{}'.
解题方法
要判断一个字符串 s 是否是有效的括号组合,可以使用栈(Stack)这一数据结构来处理。
解决方法步骤:
- 遍历字符串
- 使用栈来储存左括号:每当遇到一个左括号
(,{,[, 就将它压入栈中。 - 匹配右括号:每当遇到一个右括号
),},],从栈中弹出栈顶元素并检查是否与当前右括号匹配。如果匹配,则继续。如果不匹配,或者栈为空,则说明字符串无效。 - 检查栈是否为空:遍历完字符串后,如果栈为空,说明所有的括号都匹配成功,字符串是有效的;否则,字符串无效。
代码实现
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
155. Min Stack
题目描述
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
Implement the MinStack class:
MinStack()initializes the stack object.void push(int val)pushes the elementvalonto the stack.void pop()removes the element on the top of the stack.int top()gets the top element of the stack.int getMin()retrieves the minimum element in the stack.
You must implement a solution with O(1) time complexity for each function.
Example 1:
1 | Input |
Constraints:
-2^31 <= val <= 2^31 - 1- Methods
pop,topandgetMinoperations will always be called on non-empty stacks. - At most
3 * 10^4calls will be made topush,pop,top, andgetMin.
解题方法
使用一个辅助栈 min,用于存取 stack 中最小值。
代码实现
1 | class MinStack: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(1)$ :压栈,出栈,获取最小值的时间复杂度都为 O(1)。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$ :包含 n 个元素辅助栈占用线性大小的额外空间。
394. Decode String
题目描述
Given an encoded string, return its decoded string.
The encoding rule is: k[encoded_string], where the encoded_string inside the square brackets is being repeated exactly k times. Note that k is guaranteed to be a positive integer.
You may assume that the input string is always valid; there are no extra white spaces, square brackets are well-formed, etc. Furthermore, you may assume that the original data does not contain any digits and that digits are only for those repeat numbers, k. For example, there will not be input like 3a or 2[4].
The test cases are generated so that the length of the output will never exceed 10^5.
Example 1:
1 | Input: s = "3[a]2[bc]" |
Example 2:
1 | Input: s = "3[a2[c]]" |
Example 3:
1 | Input: s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef" |
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 30sconsists of lowercase English letters, digits, and square brackets'[]'.sis guaranteed to be a valid input.- All the integers in
sare in the range[1, 300].
解题方法
要解码一个按照指定规则编码的字符串,可以使用栈结构来处理。具体步骤如下:
初始化栈:创建一个栈用于存放字符和数字。
遍历字符串:依次处理字符串中的每个字符。
- 如果是数字,则构建完整的重复次数
k(可能由多位数字组成)。 - 如果是左方括号
[,将当前构建的数字k压入栈,并开始一个新的编码上下文。 - 如果是右方括号
],则从栈中弹出最近的字符串和重复次数,进行解码并将结果放回栈中。 - 如果是字母,则直接将其添加到当前的解码字符串中。
- 如果是数字,则构建完整的重复次数
构建最终结果:遍历结束后,栈中将只剩下一个解码后的字符串,作为最终结果返回。
代码实现
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
739. Daily Temperatures
题目描述
Given an array of integers temperatures represents the daily temperatures, return an array answer such that answer[i] is the number of days you have to wait after the i^th day to get a warmer temperature. If there is no future day for which this is possible, keep answer[i] == 0 instead.
Example 1:
1 | Input: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: temperatures = [30,40,50,60] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: temperatures = [30,60,90] |
Constraints:
1 <= temperatures.length <= 10^530 <= temperatures[i] <= 100
解题方法
题目的意思实际上就是给定一个数组,每个位置上有整数值。对于每个位置,在该位置右侧找到第一个比当前元素更大的元素。求「该元素」与「右侧第一个比当前元素更大的元素」之间的距离,将所有距离保存为数组返回结果。
最简单的思路是对于每个温度值,向后依次进行搜索,找到比当前温度更高的值。
更好的方式使用「单调递增栈」,栈中保存元素的下标。
解题思路:
- 将答案数组
ans全部赋值为0,然后遍历数组每个位置元素。 - 如果栈为空,则将当前元素的下标入栈。
- 如果栈不为空,且当前数字大于栈顶元素对应的数字,栈顶元素出栈,计算下标差。
- 此时当前元素就是栈顶元素的下一个更高值,将其下标差存入
ans数组中保存起来,判断栈顶元素。 - 直到当前数字小于或等于栈顶元素,则停止出栈,将当前元素下标入栈。
- 输出数组
ans。
代码实现
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
题目描述
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
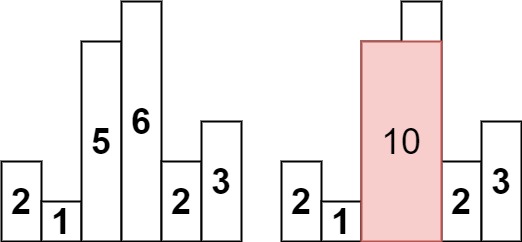
1 | Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] |
Example 2:
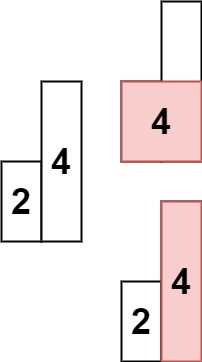
1 | Input: heights = [2,4] |
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 10^50 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
解题方法
这个问题是经典的「最大矩形面积」问题,可以通过使用栈来有效地解决。
思路:
栈的应用:
- 我们遍历整个高度数组
heights,并使用栈来存储柱子的索引。栈中保持的是按高度递增的顺序。 - 如果当前柱子的高度大于栈顶的柱子高度,说明可以继续加入栈中;如果当前柱子的高度小于栈顶的柱子高度,说明之前的柱子可以计算出矩形的面积了。
- 我们遍历整个高度数组
如何计算面积:
- 当遇到一个比栈顶柱子低的柱子时,我们可以出栈,计算出以栈顶柱子为最矮柱子的矩形的面积。矩形的宽度是由当前柱子的索引与栈顶柱子的前一个索引决定的。
最后处理栈中的剩余柱子:
- 如果栈中还有剩余的柱子,说明这些柱子的高度一直延伸到了数组的末尾,我们需要再一次进行面积计算。
代码实现
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:每个元素最多被推入栈一次,也最多被弹出一次,因此时间复杂度是 $O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是柱子的数量。
空间复杂度:由于使用了栈来存储柱子的索引,空间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
