前言
题单LeetCode 热题 100的二叉树部分,给出解析。
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [1,null,2,3] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [1] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
解题方法
二叉树的中序遍历,给出递归遍历以及非递归遍历两种解法。
非递归遍历的思路如下:
- 定义一个栈。
- 将树的左节点依次入栈。
- 左节点为空时,弹出栈顶元素并处理。
- 重复 2 和 3 的操作。
代码实现
递归版
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
非递归版
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
两个方法的时间空间复杂度是一样的:
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree’s maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1,null,2] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^4]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题方法
求二叉树的最大深度,考虑使用递归和非递归的方法来解题。
递归:
从根节点
root开始递归。当节点为空时,返回深度为
0。分别递归计算左、右子树的深度。
最后返回较大深度加上
1(考虑根节点)
非递归:
非递归遍历采用「广度优先搜索」的思想,初始化一个队列,加入根节点。遍历树的每一层,每遍历到一个节点就将该节点的左右子节点加入队列,处理完一层之后深度加 1。
代码实现
递归:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
非递归:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
两个方法的时间空间复杂度是一样的:
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
226. Invert Binary Tree
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [2,1,3] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题方法
本题要求将二叉树进行翻转,即二叉树中的每个节点的左右孩子都进行互换。
给出两种实现方法:递归、队列。
递归:
将递归函数当做普通函数看待,只要思考当前层的处理逻辑,明白递归函数的输入输出是什么即可,调用的时候不需要管函数的内部实现。
invertTree(TreeNode root) 的定义:
- 此函数可以翻转一棵二叉树,将二叉树中的每个节点的左右孩子都进行互换。
- 函数的输入是要被翻转的二叉树。
- 函数的输出是翻转之后的二叉树。
函数的写法:
- 递归终止的条件:要翻转的节点为空,停止翻转,返回空节点。
- 返回值:左右子树节点翻转,根节点不变,返回根节点。
- 根节点的新左子树是原右子树,新右子树是原左子树。
队列:
利用队列遍历树的所有节点,并交换每个节点的左右子节点。
算法流程:
- 特例处理: 当 root 为空时,直接返回 null 。
- 初始化: 初始化队列,并加入根节点 root 。
- 循环交换: 当队列 queue 为空时跳出。
- 出队: 记为 node 。
- 添加子节点: 将 node 左和右子节点入队。
- 交换: 交换 node 的左 / 右子节点。
- 返回值: 返回根节点 root 。
代码实现
递归:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
其中 root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left 这种写法是利用了 Python 的多重赋值(multiple assignment)特性。这个操作会在同一时刻完成左右子节点的交换,而不会出现中间状态,这样可以避免潜在的错误。
多重赋值的工作原理:
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left 的执行顺序是这样的:
- 右侧的表达式 (
root.right, root.left) 会首先被计算并生成一个元组(root.right, root.left)。 - 左侧的变量 (
root.left, root.right) 会同时被赋值为右侧对应位置的值。
这样,就可以在不需要临时变量的情况下,交换两个变量的值。关键是因为在进行赋值操作时,Python 是先计算右侧的所有表达式,然后再一次性将结果赋给左侧变量。
使用多重赋值可以保证在同一时刻交换两个变量的值,避免在分开赋值时出现意外的覆盖问题。因此,root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left 要写在同一行。
如果要分开写,就需要加入临时变量。
队列:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
两个方法的时间空间复杂度是一样的:
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
101. Symmetric Tree
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
Example 1:
1 | Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively?
解题方法
对称二叉树定义: 对于树中_任意两个对称节点_ L 和 R,一定有:
L.val = R.val:即此两对称节点值相等。L.left.val = R.right.val:即 L 的左子节点和 R 的右子节点对称。L.right.val = R.left.val:即 L 的右子节点和 R 的左子节点对称。
给出两种实现方法:递归、队列。
递归:
定义一个递归函数:isMirror(left, right) 用来判断两个节点是否对称。
isMirror(left, right):
终止条件:
left与right都为空,两个节点都到达最底部的叶节点,则对称,返回True。left与right不都为空,有其中一个节点未到达底部叶节点,不对称,返回False。当节点
left的值不等于节点right的值,此树不对称,返回False。
递归工作:
- 判断两节点
left.left和right.right是否对称,即isMirror (left.left, right.right)。 - 判断两节点
left.right和right.left是否对称,即isMirror (left.right, right.left)。
- 判断两节点
返回值:
- 使用
and连接递归工作。
- 使用
队列:
使用一个队列来检查二叉树的左右子树是否对称,使用队列同时遍历树的左右子树,并在每一步检查节点的对称性。
- 初始:将根节点的左右子节点加入队列。
- 每次从队列中取出两个节点进行比较,如果不相等则返回
False。 - 如果两个节点都为空,继续循环;如果只有一个为空,返回
False。 - 如果两个节点相等,将它们的子节点按照对称顺序加入队列
- 将
left.left和right.right为一组。 - 将
left.right和right.left为一组。
代码实现
递归:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
队列:
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
两个方法的时间空间复杂度是一样的:
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
543. Diameter of Binary Tree
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the diameter of the tree.
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1,2] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题方法
定义一个全局变量 diameter(初始化为 0),用于记录二叉树的最大直径。
设计用于遍历二叉树的 DFS 函数:函数传入当前节点 u ,返回以该节点为根时,方向「往下」的最大路径节点数量(注意这里是点数,而不是题目要求的边数)。
单次执行流程中,先递归处理当前节点 u 的左右节点,得到左右子树为根时的“往下”最大路径 left_height 和 right_height,两者中的较大值 +1 即是本次执行流程的返回值(+1 的含义是在子路径基础上增加当前节点)。
同时,left_height + right_height 则是以当前节点 u 为路径最高点时的路径长度,用此更新全局 diameter 即可。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(1)$
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题方法
题目要求我们对给定的二叉树进行层序遍历,也就是从上到下,从左到右地依次访问每一层的结点,并返回每一层的节点值列表。
层序遍历通常使用广度优先搜索(BFS),通过一个队列(Queue)来实现。具体步骤如下:
- 初始化一个队列:
- 首先将根节点加入队列。
- 每次从队列中取出当前层的所有节点,记录这些节点的值,然后将他们的左右子节点(如果存在)依次加入队列中。
- 逐层遍历:
- 队列用于保存每一层的所有节点。在处理每一层节点时,我们将当前队列的长度保存下来(代表当前层的节点数),然后依次从队列中取出这些节点并记录它们的值。
- 处理完当前层后,再将下一层的所有节点加入队列中,重复这个过程直到队列为空。
- 终止条件:
- 当队列为空时,表示所有层都已经遍历完成,返回结果即可。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
- 队列初始化:我们使用
deque进行队列操作,初始时将根节点root加入队列。 - 层序遍历:在
while循环中,每次处理一层的所有节点,使用level_size保存当前层的节点数,并逐个将节点从队列中取出,记录它们的值。 - 处理左右子节点:如果当前节点有左或右子节点,则将这些子节点加入队列,以便下一层进行处理。
- 最终输出:每处理完一层,就将这一层的节点值列表加入
result,最后返回result。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
题目描述
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order , convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] |
Example 2:
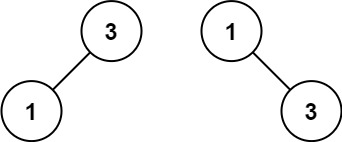
1 | Input: nums = [1,3] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
解题方法
这个问题要求将一个已排序的整数数组 nums 转换成一个 高度平衡的二叉搜索树 (BST)。我们可以通过分治法来实现这个转换,具体方法是递归地选择数组的中间元素作为树的根节点,然后分别构造其左子树和右子树。由于数组是有序的,选择中间元素作为根节点能够保证树的平衡。
解决思路:
- 选择中间元素作为根节点:
- 由于数组是排序好的,选择中间元素作为根可以确保左右子树的节点数量大致相等,从而保持树的平衡。
- 递归构造左右子树:
- 左子树对应数组中中间元素左边的部分。
- 右子树对应数组中中间元素右边的部分。
- 递归的终止条件:
- 当数组为空时,返回
null,表示子树为空。
- 当数组为空时,返回
算法步骤:
- 找到当前数组的中间元素,创建一个新节点作为树的根。
- 递归地构建左子树,使用数组中间元素左边的部分。
- 递归地构建右子树,使用数组中间元素右边的部分。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是数组的长度。每个元素都只被访问一次,因此时间复杂度是线性的。
空间复杂度:$O(log n)$,由于递归调用栈的深度是树的高度,而对于一个平衡的二叉搜索树,树的高度是 $log n$。
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
A valid BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [2,1,3] |
Example 2:

1 | Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
解题方法
要判断一棵树是否为二叉搜索树,我们可以使用递归以及中序遍历的方法。
递归
我们可以使用递归的方法来遍历整棵树,同时确保每个节点的值在一个有效的范围内。初始时,根节点的值应在 (-∞, ∞) 范围内。随后:
- 左子节点的值应该在
(-∞, 当前节点的值)范围内。 - 右子节点的值应该在
(当前节点的值, ∞)范围内。
详细步骤:
- 定义一个辅助函数,传入当前节点以及该节点的允许值范围(
min_val, max_val)。 - 对于每个节点,进行以下判断:
- 如果节点为空(即
None),返回True(空树是一个有效的 BST)。 - 如果当前节点的值不在允许范围内,返回
False。 - 递归检查左子树和右子树,更新左子树和右子树的范围。
- 如果节点为空(即
- 如果所有节点都符合条件,则返回
True。
中序遍历
基于二叉搜索树(BST)的一个性质:对一棵二叉搜索树进行中序遍历时,得到的值序列应该是严格递增的。
思路:
- 使用中序遍历(左 -> 根 -> 右),依次遍历每个节点。
- 记录上一个遍历的节点值,并与当前节点的值比较。如果当前节点的值不大于上一个节点的值,则该树不是 BST。
- 如果所有节点都满足严格递增的条件,则是一个有效的 BST。
代码实现
递归
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
中序遍历
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
两个方法的时间空间复杂度是一样的。
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(h)$(h 为树的高度,这是递归调用栈的深度)
230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
题目描述
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the k^th smallest value ( 1-indexed ) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
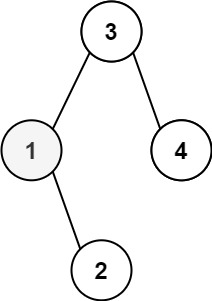
1 | Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 |
Example 2:
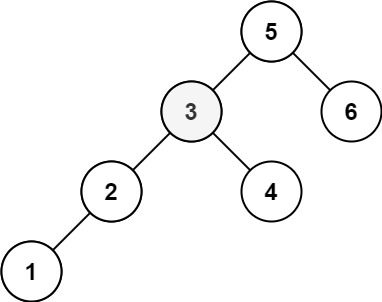
1 | Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 10^40 <= Node.val <= 10^4
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
解题方法
给定一棵二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个整数 k,要求返回树中第 k 小的节点值。这里的 k 是索引,即第 k 小的值是最小的节点值。
中序遍历:由于二叉搜索树的中序遍历结果是节点值的升序排列,因此我们可以通过中序遍历遍历树,访问每个节点并记录它们的值。当遍历到第 k 个节点时,我们就得到了第 k 小的节点值。
我们可以通过递归的方式进行中序遍历,同时记录访问的节点数,当访问到第 k 个节点时,立即返回其值,避免不必要的遍历。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1,null,3] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题方法
使用 DFS,通过递归的方式遍历二叉树,同时我们可以利用一个全局的变量记录当前访问的层数。当我们访问每一层时,只有第一个访问到的节点(即最右边的节点)会被记录下来。
- 使用 DFS 遍历树,在递归过程中从右子树开始访问。
- 对于每一层,只有第一次访问到该层时,才记录节点值(因为我们先访问右子树,确保最右边的节点最先被记录)。
- 递归到左子树。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是二叉树的节点数,每个节点都会被访问一次。
空间复杂度:$O(h)$,其中 $h$ 是树的高度。
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
- The “linked list” should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
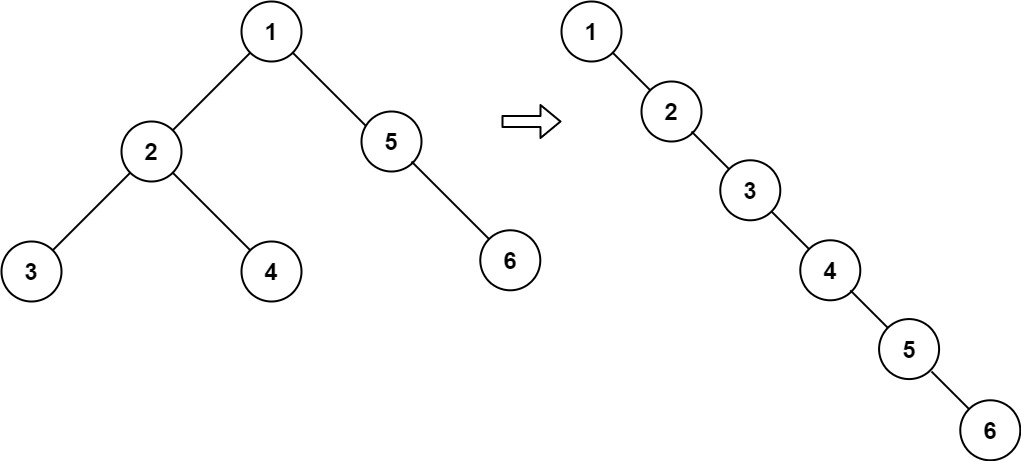
1 | Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [0] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
解题方法
这个问题的目标是将一个二叉树按照前序遍历的顺序展平为一个链表。在这个链表中,每个节点的 right 指针指向下一个节点,left 指针为 null。
思路:
前序遍历:首先,我们需要按前序遍历的顺序(根 -> 左 -> 右)来展平二叉树。这样每个节点的
right指针会指向下一个节点。链表结构:展平后树的形态会像一个链表,所有的节点只有
right指针指向下一个节点,left指针为null。原地修改:为了使得空间复杂度为
O(1),我们必须在原地修改树结构,不使用额外的数据结构来存储节点。
我们采用逆先序遍历的顺序(右 → 左 → 根),先构造链表的「尾部」,再不断将前一个节点插到当前链表的「头部」。
每处理一个节点 node,把它的 right 指向之前处理过的 prev,这就构成了从尾到头的链表。
考虑采用递归解法,在递归方法中,我们可以按如下步骤进行:
- 对当前节点进行前序遍历。
- 递归处理当前节点的左子树,将其展平。
- 递归处理当前节点的右子树,将其展平。
- 将当前节点的左子树连接到右子树,最后将左子树置为
null。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是树中的节点数量。每个节点最多被访问一次。
空间复杂度:$O(h)$,其中 $h$ 是树的高度。递归调用栈的最大深度为树的高度。
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
题目描述
Given two integer arrays preorder and inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Example 1:

1 | Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] |
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorderandinorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
inorderalso appears inpreorder. preorderis guaranteed to be the preorder traversal of the tree.inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
解题方法
这个问题是关于根据二叉树的前序遍历(preorder)和中序遍历(inorder)数组来重建二叉树的问题。在二叉树中,前序遍历的顺序是先访问根节点,然后是左子树,最后是右子树;中序遍历的顺序是先访问左子树,然后是根节点,最后是右子树。
以下是解决这个问题的算法步骤:
- 前序遍历的第一个元素总是树的根节点。
- 在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置,这将中序遍历分成两部分,左边是左子树的中序遍历,右边是右子树的中序遍历。
- 根据根节点在中序遍历中的位置,可以确定左子树和右子树的节点数量。
- 在前序遍历中,根节点之后的部分可以分成两部分,对应于左子树和右子树的前序遍历。
- 递归地对左子树和右子树应用相同的过程。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(n)$
437. Path Sum III
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Example 1:
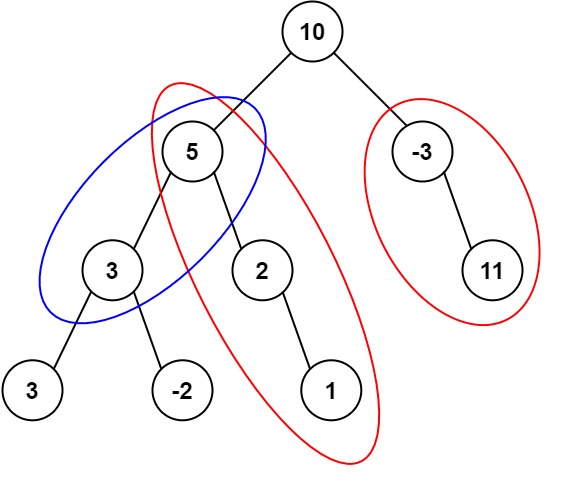
1 | Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 1000]. -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
解题方法
要解决这个问题,我们可以使用深度优先搜索(DFS)遍历二叉树的每个节点,并利用一个哈希表来存储从根节点到当前节点路径上的累积和。这样我们可以快速判断是否存在子路径的和等于目标和 targetSum。
解题方案:
- 使用 DFS 从根节点开始遍历二叉树的每个节点。
- 在遍历时,记录从根节点到当前节点的累积和。
- 对于每个节点,计算是否存在一个子路径(以当前节点为结束点)的路径和等于
targetSum。 - 使用哈希表记录已经遍历过的路径的累积和,查找是否存在
currentSum - targetSum,这意味着存在一个从之前某个节点到当前节点的路径和为targetSum。 - 递归地遍历左右子树。
- 回溯时,从哈希表中移除当前节点的累积和,避免影响其他分支。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$:每个节点仅访问一次,更新和查询哈希表的操作都是常数时间。
空间复杂度:$O(h)$,其中 h 是树的高度。在最坏情况下,树可能是单链表状。
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
题目描述
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:

1 | Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 |
Example 2:

1 | Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 10^5]. -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9- All
Node.valare unique . p != qpandqwill exist in the tree.
解题方法
本题要求找到树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先:
最近公共祖先的定义:设节点
root为节点p,q的某公共祖先,若其左节点root.left和右子节点root.right都不是p,q的公共祖先,则称root是最近的公共祖先。
则若 root 是 p, q 的最近公共祖先:
p和q在root的子树中,且分列于root的_异侧_(分别在左右子树中);p = root,且q在root的左或右子树中;q = root,且p在root的左或右子树中;
通过递归对二叉树进行先序遍历,当遇到节点 p 或 q 时返回。从底向上回溯,当节点 p, q 在节点 root 的异侧时,节点 root 为最近公共祖先,则向上返回 root。
递归解析:
- 终止条件:
- 越过叶节点,返回
null; - 当
root等于p,q,则直接返回root;
- 越过叶节点,返回
- 递归过程:
- 递归左节点,返回值为
left; - 递归右节点,返回值为
right;
- 递归左节点,返回值为
- 返回值:根据
left和right,分析情况:left与right同时为空,说明root的左/右子树中都不包含p,q,返回null;left与right同时不为空,说明p,q分别在root的异侧(分别在左/右子树),因此root是最近公共祖先,返回root;- 当
left为空,right不为空,说明p,q都不在root的左子树中,直接返回right,分为两种情况:p,q其中一个在root的右子树中,此时right指向p(假设为p);p,q两节点都在root的右子树中,此时right指向最近公共祖先节点;
- 当
left不为空,right为空,同上;
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$(节点个数)
空间复杂度:$O(n)$(递归调用栈)
124. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
题目描述
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once . Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
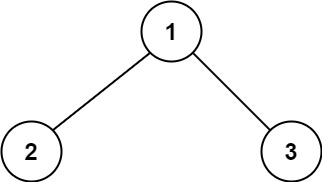
1 | Input: root = [1,2,3] |
Example 2:
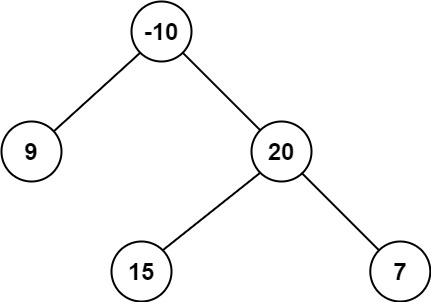
1 | Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 10^4]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题方法
要解决这个问题,我们需要计算二叉树中任何可能路径的最大路径和。路径可以从任意节点开始和结束,并且路径上每个节点只能出现一次。
解决思路:
这个问题可以通过递归的方法来解决,我们需要定义一个辅助函数,该函数计算当前节点为根的子树中的最大路径和。为了计算每个节点为根的最大路径和,我们需要考虑以下几个情况:
- 当前节点的值。
- 通过左子树的最大路径和(左子树提供的最大贡献值)。
- 通过右子树的最大路径和(右子树提供的最大贡献值)。
- 当前节点加上左子树和右子树提供的最大贡献值。
在每个节点,我们都需要计算这个节点为根的路径是否能提供更大的路径和,同时,我们还需要返回一个值,表示从当前节点开始向上延伸的最大路径和,以供其父节点使用。
具体步骤:
递归函数定义:
定义一个递归函数max_gain(node),表示从节点node出发向上的最大路径和。如果节点为空,返回0。递归计算左右子树的最大贡献值:
计算左子树和右子树的最大贡献值,若为负值则直接舍弃(置为0)。更新全局最大路径和:
计算当前节点加上左右子树的贡献值的路径和,并更新全局最大路径和。返回给父节点的最大贡献值:
计算当前节点能向父节点提供的最大贡献值(即node.val + max(left_gain, right_gain)),并返回。处理根节点:
最终在根节点执行上述递归函数即可得到整个树中的最大路径和。
代码实现
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
空间复杂度:$O(logn)$
